Precision Metal Part Design
What is Computer Aided Design used for in Metal Manufacturing?
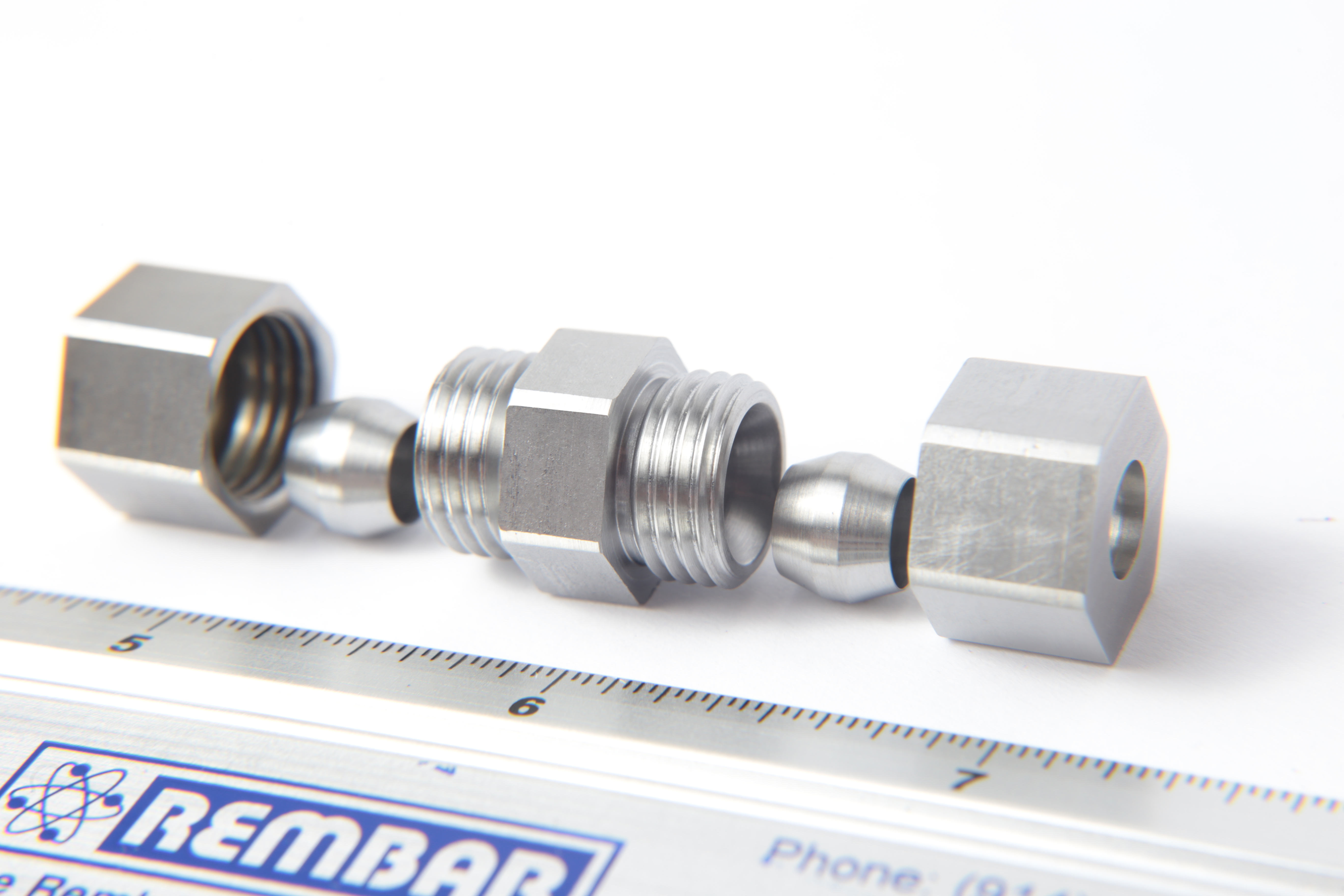
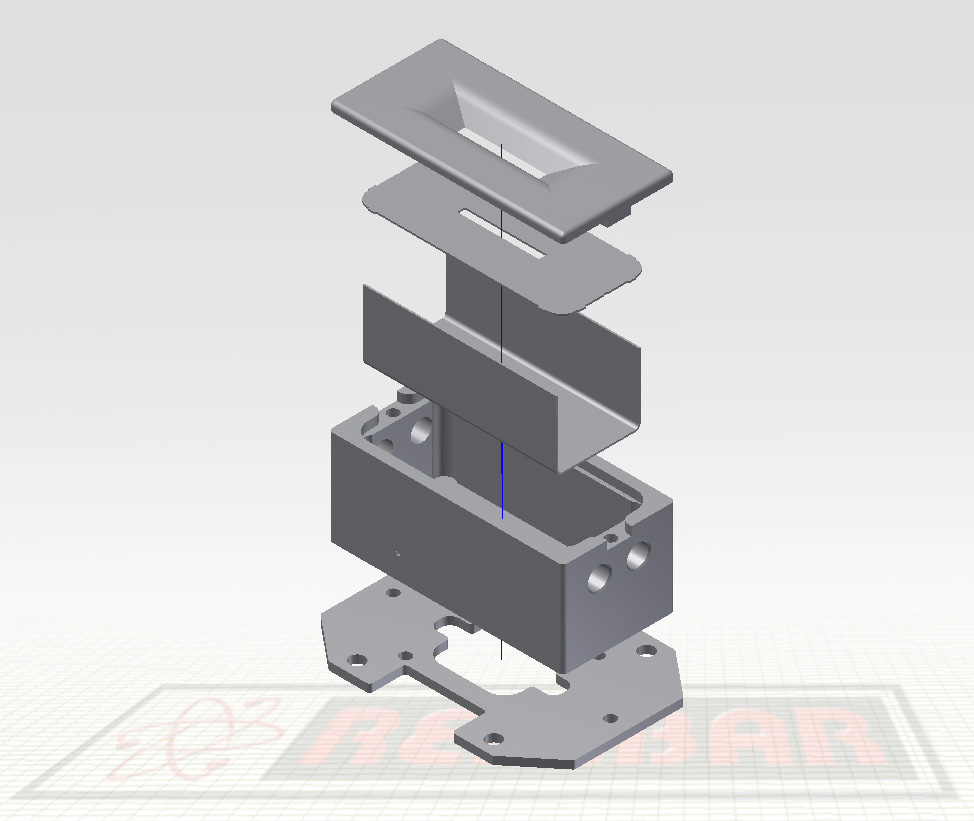
Computer aided design or CAD is part of the initial steps in visualizing your part or component. This involves using computer software to create a 3D image that maps out the shape and dimensions of the desired part. The use of CAD models in metal manufacturing in conjunction with computer aided manufacturing (CAM) allows fabrication companies to craft metal parts with extreme detail and precision.
A major benefit of using CAD is that it lets you check the tool path before the material is cut, saving you the cost of making an incorrect cut into an expensive metal. CAD simulation also lets you identify how long production runs will take, which is great for projecting supply and delivery times.
Need assistance with your design? Rembar offers consulting over design and material usage to help clients achieve the necessary structural integrity for their parts at the most cost efficient price.


Bring Your Project From Design to Reality
From well thought out designs to concept sketches on napkins, we’ve helped clients with projects in all stages of development. Regardless of if you know the exact specs of your part or need our help, we’ll work with you to draw something up and consult you on what solutions will provide the best results.
Sometimes you already have the part you need, but need to mass produce it. With our coordinate measuring machine (CMM), we’re able to reverse engineer and replicate your part down to the last cut.
Advantages of CAD, CAM, and CMM
Using the latest in computer-aided design and manufacturing tools provides many advantages in comparison to manual design drafting and fabrication processes. Computer assistance offers many benefits to metal fabrication including:
- Greater visualization for preproduction review
- Increased manufacturing precision and reproduction accuracy
- Reduced material waste
- Reverse engineering capabilities
- Allows for precision quality check
- Greatly increases the speed of entire fabrication process